
Getting Started with YAML: An Introduction to the Basics
Posted on 02 Feb 2023
Introduction
This article explores the fundamental concepts of YAML (YAML Ain’t Markup Language), a popular data serialization format. The topics covered include comments, on what YAML is, the difference between YAML, JSON, and XML, and the main data structures including scalars, mappings, sequences, and objects. The aim is to provide a comprehensive introduction to the basics of YAML.
Understanding YAML: What it is and Why it Matters

Photo from Youtube
YAML is a lightweight, human-readable data-serialization language. It is primarily designed to make the format easy to read while including advanced features. Its simple and clean syntax, human-friendly design, and support for complex data structures make it a versatile choice for many use cases.
YAML is similar to XML and JSON but it is less verbose, more readable, and easy to use. Many products like Ansible, Kubernetes, Puppets, Jenkins, Docker, AWS, and others use YAML for managing configuration files because it is much easier to read and less verbose than JSON and XML.
YAML files have “.yaml” or “.yml” extensions and you can edit them in whatever text editor.
YAML is similar to JSON inline style, from this point of view it can be considered a superset of JSON. For example, JSOn doesn’t support comments while YAML does.
In addition, YAML is very easy and simple to represent complex objects and data structures. Due to this, it is heavily used in configuration management.
You can find more information about YAML on its official website.
Comparing YAML to XML and JSON: Key Differences and Use Cases

Photo from https://medium.com/
XML was introduced in 1996 as a format “… for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing arbitrary data” according to Wikipedia. It is an extensible markup language that, through a Document Type Definition (DTD), allows the definition of documents that match the different grammar. For many years it has been used in Java and other languages as a data serialization or transmission (SOAP) format. However, it is quite a verbose language because it requires data to be enclosed between two tags and it is not easy to read for a human. Today it is still used as a configuration tool in many languages and operating systems such as Java and Android.
JSON (Javascript Object Notation) is a format created for data transmission between servers and browsers, especially when using the Javascript language. Precisely because it is a format that was created for data transmission, its goal is to be as least verbose as possible and clear in representing the data. For this reason, the format does not support comments. This makes JSON less suitable for representing configuration files and management even though it is used for that purpose in many contexts.
YAML in some ways is a superset of JSON, which means all the features in JSON can be found in YAML. The fact that the format is human-readable and easy to use makes it represent configuration files and management.
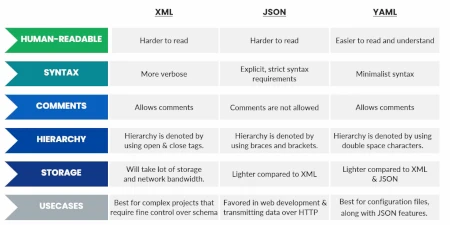
Photo from YAML Zero to Master Udemy Course
The following figure shows an example of the same data structure represented with XML, JSON, and YAML.

Online there are a lot of tools that help you to convert one format into another.
YAML: Understanding Basic Concepts
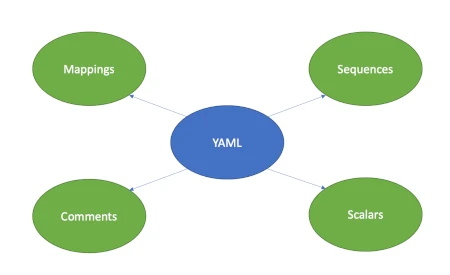
A YAML format to represent data uses the following data type:
- Scalars: The content is a primitive type like strings, numbers, boolean, and so on.
- Arrays/Lists (YAML calls them sequences): The content of a sequence node is an ordered series of zero or more nodes. In particular, a sequence may contain the same node more than once. It could even contain itself.
- Dictionaries (YAML calls them mappings): the content of a mapping node is an unordered set of key/value node pairs, with the restriction that each of the keys is unique. YAML places no further restrictions on the nodes.
In addition to this, YAML supports comments.
Representing Scalars Data in YAML: Key-Value Pairs
YAML files have a series of key-value pairs, which are used to store data. The keys and values are separated by colons and can represent primitive data types such as strings, numbers, and booleans. For example, the following YAML file represents a person’s name and age:
firstname: "John"
lastname: Doe
middlename: 'Sir'
age: 30
height: 176
weight: 75.2
male: true
positive-infinity: .inf
negative-infinity: -.inf
invalid-number: NaN
null-value: null
null-value: ~
null-value:
In this example, the name is the key, and “John” is the associated value. The name attribute is a string. YAML strings are Unicode. In most situations, you don’t have to specify them in quotes. But if we want escape sequences handled, we need to use double or single quotes. Similarly, age is the key and 30 is an integer value. YAML supports also floating points.
Boolean values are “true” and “false”, but you can use also “yes” and “no” or “on” and “off” because internally YAML converts them into “true” and “false”.
There are special scalar values in YAML you can use like positive and negative infinity numbers, null values, and invalid numbers.
Comments
You can comment contents of a YAML file using the # character as shown below.
# This is a comment on the first.
# And this is a commented second line.
Organizing Data with Sequences: A Guide to Structuring Arrays
YAML also supports lists and arrays, which can be represented as follows:
fruits:
- apples
- bananas
- oranges
In this example, the key “fruits” is associated with a list of three items: apples, bananas, and oranges. This simple syntax makes YAML easy to read and write for both humans and machines.
There are two styles to represent sequences: block and flow. The following example shows both:
# Sequences in Block Style
legumes:
- peas
- beans
- lentils
fruits:
- apples
- bananas
- oranges
fruits:
- apples
- bananas
- oranges
# Sequences in Flow Style
places: [sea, mountain, "hill"]
It is possible to nest sequences in the element of a sequence as follows. In the example, a company could sell three types of products: Cars, Motorbikes, and Bikes. Then in the Car category, it can sell Jeep, Ferrari, and Lamborghini.
# Sequences in Block Style
products:
- Cars:
- Jeep
- Ferrari
- Lamborghini
- Motorbikes:
- "Harley-Davidson"
- Honda
- Ducati
- Bikes:
- Mountain Bike
- "Trek bike"
Dictionaries in YAML: Storing Key-Value Pairs in a Collection
In YAML, dictionaries are a collection of key-value pairs that are used to store data. YAML calls dictionaries as “mappings” and they are useful to represents complex data structure like Person, Vehicle, Car, etc. An object in YAML is represented using nested key-value pairs, where each key-value pair represents an attribute of the object. For example, consider the following YAML representation of a person object with name and address attributes:
person:
name: John Doe
address:
street: 123 Main St.
city: Anytown
state: CA
zip: 90210
In YAML, you can organize dictionaries in sequence. For example, if you want to describes a list of three people you can write something like this:
people:
- name: Mary jane
age: 30
male: No
- name: Jane Doe
age: 28
male: Yes
In this example, the key “people” is associated with a dictionary of two key-value pairs, each representing a person with a name and age attribute. This syntax allows for the easy representation of collections of data, such as lists of people, products, or any other type of data.
Dictionaries in YAML are useful for grouping related data together and for easily accessing individual items within the collection. The ability to store data in dictionaries and retrieve it based on the keys makes YAML a powerful and flexible data serialization format.
Conclusion
In conclusion, YAML is a popular and human-readable data serialization format that provides a simple and efficient way to represent data structures and primitive data types. This article covered the basics of YAML, including primitive data types like strings, numbers, and booleans, as well as more complex data structures like dictionaries, sequences, and objects. In the next article, we will cover more advanced concepts about YAML.


