
Getting started with Cloud Computing
Posted on 01 Jan 2019
In this article, I would like to talk about Cloud Computing. I will try to explain what it really is, its advantages and its main characteristics.
Traditional IT Overview
A Simple Web Application
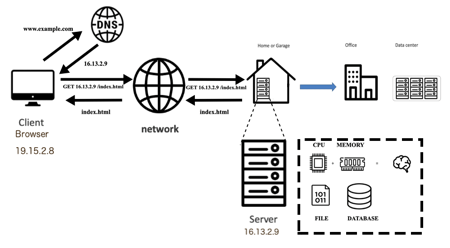
Before to start let’s explain how a web application works in the traditional IT world. Imagine the application is a simple static website www.example.com with a single home page (index.html). A user types the domain in the browser’s address bar, the application asks a DNS server to translate that mnemonic name into an IP address. Then, the browser sends a GET request over the HTTP protocol to the 16.13.2.9 server for its home page. Finally, the request goes over the Internet, arrives at the server that replies back with the index.html file.
A server is a computer with its own CPU and Memory (its Brain) and a long-term storage system (i.e. files or database) where there is the index.html file.
The Problem with the Traditional IT
Imagine you are Sergey Brin in the ’90 and you have a bright idea for a web application. In that era, probably you would have started your business in the garage of your home.
However, to make it available over the Internet you needed to set up a server, power it up, cable all the network devices, configure disks, provide 27×7 support, and much more. All this infrastructural work is not your core business but it is required if you want to make available your idea over the Internet.
Now if your idea is really bright like Google, probably your business grows and you need to add more servers and create a more complex architecture. Probably you need to move into an office and create a data center for your servers.
The questions now are: why you should care about infrastructure when your core business is just providing a service to your users? Why waste your time with IT tasks, network architectures, servers, and so on? Is it possible to reduce the time to market? Is it possible to externalize all this stuff?
The answer is Yes. The solution is Cloud Computing.
In recent years, the demand to reduce software applications’ time to market is increasing. Business owners spend the majority of their time managing infrastructure and stuff that were outside their business scope. Why manage an infrastructure if there are software companies that can do it better at a lower cost? From here the idea to let big companies (i.e. Amazon, IBM, Google, and others) do what they do the best: manage infrastructure. This will allow business owners to focus on their real business.
What is Cloud Computing?
This is the definition of Cloud Computing according to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST):
Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. This cloud model is composed of five essential characteristics, three service models, and four deployment models.

Cloud computing provides a simple way to access servers, storage, databases, and a broad set of application services over the Internet with a pay-as-you-go pricing model. With cloud computing, you don’t need to make large up-front investments in hardware and spend a lot of time managing it. Instead, you can provision exactly the right type and size of computing resources you need to power your newest bright idea.
In order to better understand what Cloud Computing means, we go through the five essential characteristics, the three service models, and the four deployment models.
Five essential characteristics
A system to comply with the Cloud Computing model needs to meet five essential characteristics:
- On-demand self-service. A user must have the possibility to request a resource or service (i.e. a virtual machine, a database, or other), without the intervention of the Cloud provider support. If, for example, the user wants a virtual machine with certain characteristics, he must be able to access a web page and order it with a mouse click.
- Broad network access. All the resources or services we order through the system must be accessible through the network and usable by any client (i.e. telephone, PC, tablet, or other).
- Resource pooling. All resources and services (i.e. storage, network bandwidth, memory, database, etc) made available by the system are organized in pools in a multi-tenant model. Each time a user requests a resource or service, it is removed from the pool and assigned to the user. The user will not have a sense of where these resources or services are located.
- Rapid elasticity. All the resources or services made available to the user in a multi-tenant model can be assigned according to requests or automatically and released just as easily when they are no longer needed.
- Measured service. The resources and services allocated to the user are constantly monitored to understand their use and, possibly, to scale them automatically or on-demand.
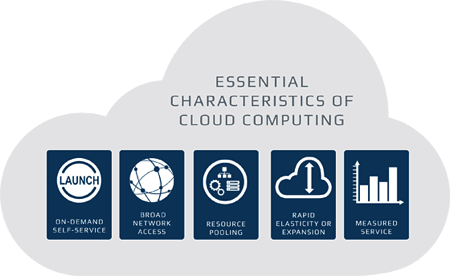
Photo from http://moderncloudcomputing.blogspot.com
Five service models
The Cloud Computing service models are essentially five:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS);
- Containers as a Service (CaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS);
- Function as a Service (FaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS).
Traditionally, the first models on the market were IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. To understand the difference between these three models, it is important to take a look at the following figure.
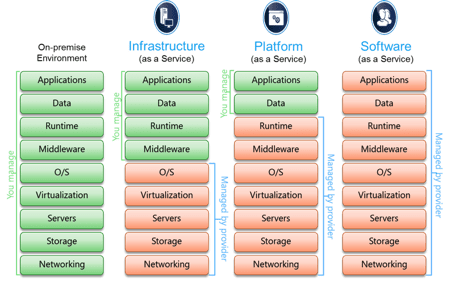
It helps us to understand the real problem that we are trying to address with Cloud Computing. Basically, before the Cloud a business owner to turn his idea into reality needed to manage an infrastructure that distracted him from his real goal. Cloud Computing’s goal is precisely to turn ideas into products or services in the shortest time possible.
Suppose you are a business owner that has an idea and wants to transform it into a software product. In the following section, you’ll see what happens in the three services model.
Traditional On-Premise Environment
As explained above, in the traditional On-Premise Environment, you will manage the whole application stack. You have to buy a server, rent a place where to keep it, connect it to power and the network, connect the disks, install the operating system and possibly the middleware (i.e. Tomcat) and the runtime (i.e. Java), and only when everything is ready (which usually requires months of work) you can focus on your application code and data. In addition, you will also be responsible for maintaining the entire stack, which means upgrading the hardware if the business grows, patching the operating system, middleware, and runtime updates as well as any security patches.
IaaS model
In the IaaS model, the Cloud system will provide Compute, Storage, and Network. For example, it gives you the possibility to order a virtual machine in a few minutes, deploys it in a network, attach a disk to it, and run a basic operating system.
PaaS model
In the PaaS model, in addition to the physical devices and the operating system, the Cloud system is also responsible to provide middleware (i.e. Tomcat) and Runtime (i.e. JDK) for your applications. You will no longer have to worry about maintaining these two additional stack levels because the system itself will take care of them. In addition, a PaaS platform often provides additional services that the application can use out of boxes such as databases, artificial intelligence, security, blockchains, and much more.
SaaS model
In the SaaS model, the application itself with its data will also be managed by the Cloud system. You can use it out of the box without having any knowledge of where this application runs and where the data resides. A typical example of a SaaS application is Gmail.
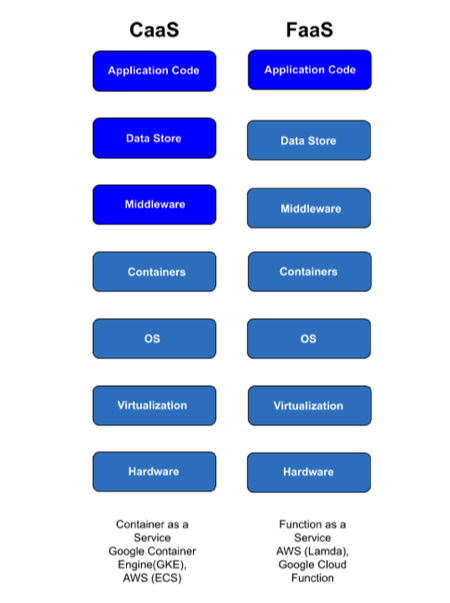
Containers as a Service (CaaS) and Function as a Service (FaaS) models
In recent years, new service models were born in Cloud offerings: Container as a Service (CaaS) and Function as a Service (FaaS).
In the CaaS model, a new Containers layer exists that manages containers using tools like Kubernetes, Docker, and others. The platform is responsible to manage the lifecycle of the Container services while the customer is responsible for the containerized applications.
In the FaaS model, the platform is responsible to manage the data and the customer will be responsible only to write application functions that will run specific tasks.
The Shared Responsibility Model
When people approach the Cloud world they have a lot of questions about the responsibility of the activities to run on the system. For example, who is responsible to keep an operating system updated? Who should apply security patches? Who is responsible for the compliance of a machine? There could be millions of questions like this, and the answer to them is only one: it depends on the service model.
In the services models above there is a precise separation of duty between the Cloud provider and the customer. For example, in the IaaS service model, the Cloud provider allows you to create a VM instance with an Operating System running on it. In AWS, for example, if you choose Linux Ubuntu then you’ll be responsible to keep it up to date.
In a PaaS service model, the Cloud Provider will be responsible for the middleware and runtime as well, while the customer will be responsible for the application and data.
Therefore, whenever you have doubts about the responsibility of actions, consider the service model you are adopting, consider the separation of duty above in order to find an answer to your doubts.
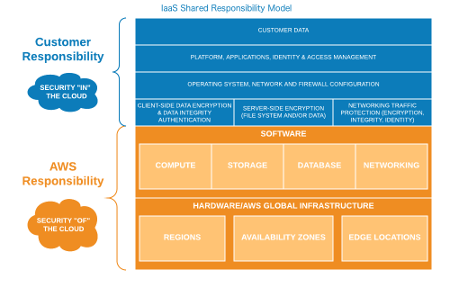
Photo from https://www.percona.com
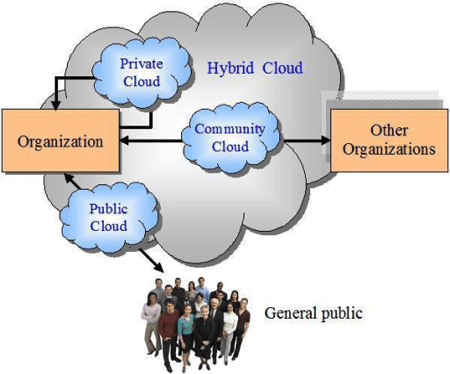
Four deployment models
Cloud Computing systems can be deployed according to four deployment models:
- Public cloud. The Cloud is publicly accessible on the Internet. A user who needs a resource (i.e. virtual machine, database) can subscribe to the platform, order the resources or services that he/she needs, pay the bill and start using it.
- Private cloud. Some companies or organizations may need to have exclusive use of their Cloud system including resources, services, and applications. These resources or services can be managed by the company or organization itself or by the Cloud provider.
- Community cloud. In this deployment model, a community, consisting of one or more organizations or one or more companies, makes available the Cloud system. Typically, these communities have a specific mission and rules to which all members adhere.
- Hybrid cloud. It can be the combination of two or more cloud systems (public, private, community) that are seen as a single entity but which, in reality, are held together by standard or proprietary technologies.
Global Infrastructure
One of the advantages of the Cloud platform is to go global in minutes and create resilient applications using services replicated in multiple availability zones. This is achieved using the Cloud Providers’ Global Infrastructure. Usually, they deploy their platform over multiple Regions on the globe.
The following figure shows an example of the Amazon Web Services (AWS) Global Infrastructure.
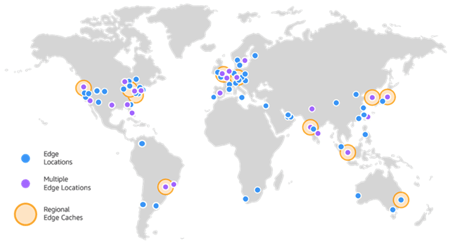
The basic idea is that applications, services, and data should live as close as possible to customers in order to reduce latency. However, not necessarily all applications, services, and data are replicated over multiple regions. Each region can have one or multiple Availabilities Zone (AZ). An Availability Zone has one or more data centers connected to each other with a low latency network.
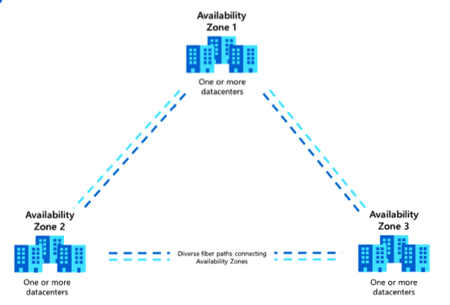
The basic idea is that a service can be replicated over multiple data centers so that it will be resilient even to unexpected data center shutdown.
Security and Compliance
Customers with traditional On-Premis systems in addition to managing hardware infrastructure, need to take care of security and compliance as well. This has a huge cost because they need to define the security guidelines, deploy and maintain tools to monitor it.
Cloud Provider provides security and compliance built-in in their architecture with almost no cost for customers. Obviously, depending on the service models there could be security and compliance aspects that are under customer responsibility.
As a customer, you inherit all the best practices of policies, architecture, and operational processes built to satisfy the requirements of most security-sensitive customers.
Using a Cloud platform you will have several benefits from a security and compliance point of view:
- Keep Your Data Safe. The infrastructure puts strong safeguards in place to help protect your privacy. In fact, all data is stored in highly secure data centers.
- Meet Compliance Requirements. Cloud providers manage dozens of compliance programs in their infrastructure. Therefore, this means that segments of your compliance have already been completed.
- Save Money. Cut costs by using cloud provider data centers. Maintain the highest standard of security without having to manage your own facility
- Scale Quickly. Security scales with your cloud usage. No matter the size of your business, the cloud provider infrastructure is designed to keep your data safe.
The 6 benefits of Cloud Computing
The 6 main benefits offered by the Cloud platforms are:
- Trade capital expense (CAPEX) for the operational expense (OPEX). Cloud computing eliminates capital expenditures associated with the purchase of hardware and software. In Cloud Computing you can pay only when you consume computing resources, and pay only for the quantity you consume.
- Benefits from massive economies of scale. The largest cloud computing companies run on a worldwide network of secure data centers. In addition, they regularly update the latest generation of hardware in a fast and efficient way. This offers several advantages over a single enterprise data center, including reduced network latency for applications and greater economies of scale.
- Stop guessing capacity. Cloud computing provisions large amounts of computing resources in minutes, typically with just a few mouse clicks. Moreover, it provides exceptional flexibility without the pressure linked to the need to plan capacity.
- Increase speed and agility. Cloud Computing eliminates the need for many infrastructure activities, allowing IT teams to spend their time achieving more important business goals.
- Stop spending money running and maintaining data centers.
- Go Global in minutes. Leverage the Cloud Provider Cloud Infrastructure to create applications available globally in minutes as close as possible to your audience and reduce latency.
Typical Cloud Services
Cloud Providers provide a lot of services in their ecosystems you can use to build your applications. In fact, you can buy a server with storage and networking, a repository to backup your data, and much more. Let’s consider the main categories.
- Compute services. These services allow you to buy a physical or virtual server with a given capacity (CPU, Memory, etc.).
- Storage services. They allow you to buy storage to mount on your server or to use to backup your data. Cloud Provider usually provides three types of storage: block, file, and object storage.
- Networking and Content Delivery services. These services allow you to create your network and content delivery systems.
- Database services. They allow you to create a database in minutes and you should not take care of its life cycle. Moreover, the service guarantees you high availability and disaster recovery.
- DevOps services. These services allow you to easily manage your development and operations activities. In this category, for example, there are code repository services, deploy pipeline services, etc.
- IoT services. Services to manage your IoT infrastructure.
- Artificial Intelligence services. These services allow you to bring artificial intelligence into your applications.
- Mobile services. This category of services allows you to build mobile applications.
What’s Next?
In the next article, we will see how these theoretical concepts map themselves into practice by analyzing one of the most popular cloud platforms on the market.


